Have you ever wondered how quantum mechanics and quantum computing defies our everyday intuition? Below is a project I built that demonstrates one of the most mind-bending phenomena in quantum physics: quantum entanglement and its ability to violate classical physics constraints.
Live Demo
What is the CHSH Game?
The CHSH (Clauser-Horne-Shimony-Holt) game is a fascinating thought experiment that reveals the strange power of quantum entanglement. It’s a cooperative game between two players, Alice and Bob, who cannot communicate with each other but share a special resource.
The Game Rules
- A referee sends random bits x and y to Alice and Bob respectively
- Alice outputs a bit a based on her input x
- Bob outputs a bit b based on his input y
- They win if:
(a + b) mod 2 = x × y
The fascinating part? With classical strategies (no quantum physics), the maximum win rate is 75%. But with quantum entanglement, Alice and Bob can achieve approximately 85.4% – seemingly breaking the laws of classical physics!
Key Features
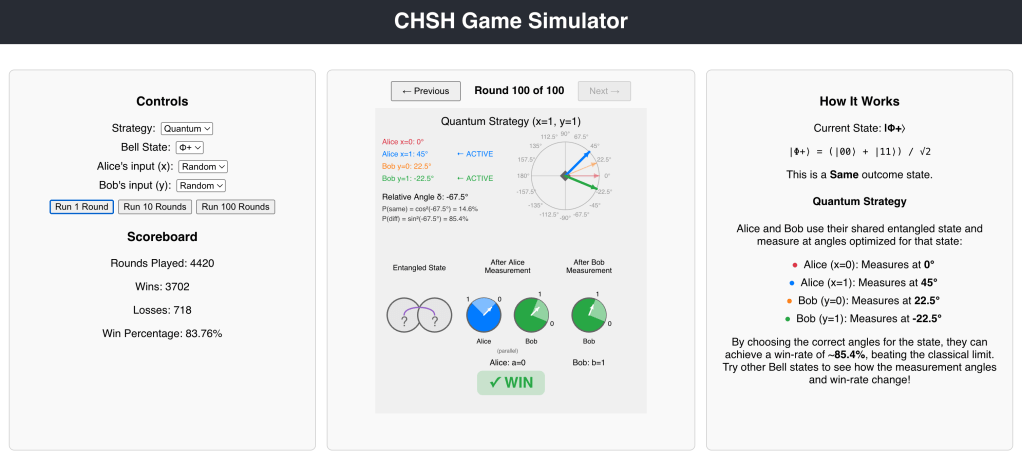
🎯 Interactive Visualization
The app features a real-time p5.js visualization that shows:
- Entangled State: Two qubits in a maximally entangled Bell state
- After Alice’s Measurement: How Alice’s measurement affects both qubits
- After Bob’s Measurement: The final collapsed state after both measurements
Each stage includes:
- Colored measurement basis quadrants (red, blue, orange, green)
- Clear labels showing measurement outcomes (0 and 1)
- Visual indication of quantum correlation (parallel or orthogonal)
🧪 Four Bell States
The simulator supports all four maximally entangled Bell states:
- |Φ+⟩ = (|00⟩ + |11⟩)/√2
- |Φ-⟩ = (|00⟩ – |11⟩)/√2
- |Ψ+⟩ = (|01⟩ + |10⟩)/√2
- |Ψ-⟩ = (|01⟩ – |10⟩)/√2
Each Bell state uses carefully optimized measurement angles to maximize the CHSH violation and achieve the theoretical ~85% win rate.
🎮 Strategy Comparison
Switch between:
- Classical Strategy: Always outputs 0, achieving the theoretical 75% maximum
- Quantum Strategy: Uses entangled qubits to beat classical limits
🎲 Flexible Input Controls
Choose input bits for Alice (x) and Bob (y):
- Random: Simulates realistic random inputs
- Fixed (0 or 1): Test specific measurement configurations
📊 Real-Time Statistics
Track performance with:
- Total rounds played
- Wins and losses
- Win percentage that converges to theoretical predictions
🔄 Round History Navigation
Navigate through previous rounds to review specific outcomes and understand the quantum measurement process better.
The Science Behind It
Bell’s Inequality and CHSH
In 1964, physicist John Bell proved that no local hidden variable theory could reproduce all predictions of quantum mechanics. The CHSH inequality is a specific formulation of Bell’s theorem:
Classical limit: S ≤ 2
Quantum mechanics: S = 2√2 ≈ 2.828
This violation proves that quantum entanglement exhibits correlations that cannot be explained by any classical mechanism, even with shared randomness!
Measurement Angles
The key to achieving the quantum advantage lies in choosing the right measurement angles. For the standard |Φ+⟩ Bell state:
- Alice’s bases: 0° (x=0), 45° (x=1)
- Bob’s bases: 22.5° (y=0), -22.5° (y=1)
The probability that Alice and Bob get the same outcome is:
P(same) = cos²(δ)
where δ is the relative angle between their measurement bases. This quantum correlation is what allows them to beat the 75% classical limit.
Orthogonal vs Parallel Correlation
Different Bell states exhibit different correlation patterns:
- Parallel correlation (|Φ+⟩, |Ψ+⟩): Qubits tend to give the same measurement outcome
- Orthogonal correlation (|Φ-⟩, |Ψ-⟩): One qubit is rotated 90° relative to the other
The simulator accounts for these differences and adjusts the probability calculations accordingly.
Try It Yourself!
You can try the simulator and explore:
- Start with the Classical strategy and run 100 rounds – you’ll see it converge to ~75%
- Switch to Quantum with the |Φ+⟩ Bell state – watch it reach ~85%
- Try different Bell states and input combinations
- Use the round navigation to review specific outcomes
Future Enhancements
- 3D Bloch Sphere Visualization: Show quantum states on the Bloch sphere using Three.js
- Animated Transitions: Step-by-step animation of the measurement process
- Educational Tutorial: Guided walkthrough explaining each concept
- Mathematical Deep Dive: Optional panel with detailed probability calculations
- Mobile Optimization: Touch-friendly controls and responsive layout
Open Source
The complete source code is available on GitHub. Feel free to:
- Explore the code
- Report issues
- Suggest improvements
- Fork and build your own quantum visualizations!
Conclusion
The CHSH game beautifully demonstrates that quantum entanglement isn’t just mathematical abstraction – it has measurable, observable consequences that defy classical intuition. This simulator makes that phenomenon interactive and accessible.
Whether you’re a physics student, educator, or simply curious about quantum mechanics, I hope this tool helps you develop an intuition for one of nature’s most fascinating phenomena.
Built with: React, p5.js, and Claude Code
Try it now: https://myhlow.github.io/chsh-game-simulator
Source code: https://github.com/myhlow/chsh-game-simulator
Have questions or suggestions? Leave a comment below or open an issue on GitHub!
You must be logged in to post a comment.